Bladder Cancer: A cancer of the bladder.
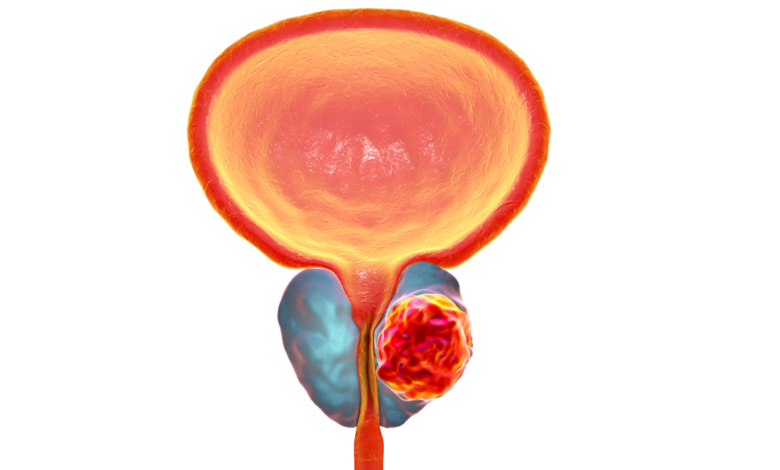
What is the Bladder Cancer ?
Bladder cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a muscular organ that stores urine before it is eliminated from the body.
What are the symptom of Bladder Cancer?
The most common symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, which can appear as red, pink, or brown. Other symptoms may include:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty urinating
- Pelvic pain
Who can suffer from Bladder Cancer?
Anyone can develop bladder cancer, but certain factors increase the risk:
- Age: The risk increases with age, particularly after 50.
- Smoking: Smoking is the most significant risk factor for bladder cancer.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as arsenic, benzene, and dyes used in the textile industry, can increase the risk.
- Family history: Having a family history of bladder cancer can increase the risk.
- Chronic bladder inflammation: Conditions like chronic cystitis or interstitial cystitis can increase the risk.
What are the type of Bladder Cancer?
There are several types of bladder cancer, based on the type of cells involved:
- Transitional cell carcinoma: The most common type, accounting for about 90% of cases.
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Less common, but more aggressive than transitional cell carcinoma.
- Adenocarcinoma: The least common type, arising from glandular cells.
Which diagnostic are available for the Bladder Cancer?
· Cystoscopy: A procedure to examine the bladder using a thin tube with a camera.
· Urine cytology: A test to examine urine cells for signs of cancer.
· CT scan or MRI: Imaging tests to assess the extent of the cancer.
What are the treatment of the Bladder Cancer?
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on the stage of the cancer and the patient’s overall health. Options include:
- Surgery: Removal of the bladder (cystectomy) or a part of the bladder (partial cystectomy).
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Intravesical therapy: Instilling chemotherapy or other drugs directly into the bladder.
Which diet should I take ,if any ?
While there is no specific diet proven to prevent or treat bladder cancer, a healthy diet can support overall health. Consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and staying hydrated are recommended.
Which speciality of the doctor will Bladder Cancer?
A urologist, a doctor who specializes in urinary tract diseases, is typically involved in the diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer.
In Bladder Cancer completely curable ?
The curability of bladder cancer depends on the stage of the cancer and the effectiveness of the treatment. Early detection and treatment significantly improve the chances of a successful outcome. Regular screenings, such as urine cytology, are recommended for individuals at high risk.