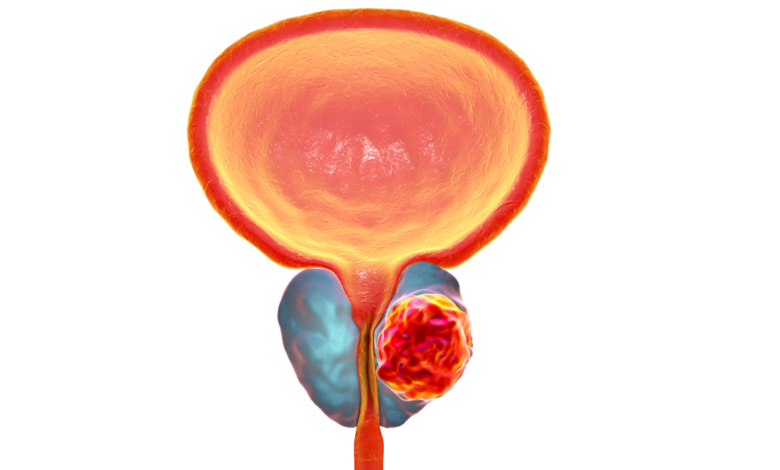
Prostate Cancer: A cancer of the prostate.
What is the Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the prostate gland, a small gland located below the bladder in men. It is one of the most common cancers in men.
What are the symptom of Prostate Cancer?
In the early stages, prostate cancer often has no symptoms. However, as the cancer grows, it can cause:
- Urinary problems: Difficulty starting or stopping urination, frequent urination, weak urine flow, or blood in the urine.
- Pain or discomfort: Pain or discomfort in the pelvis, hips, or back.
- Erectile dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
- Weight loss: Unexplained weight loss.
- Bone pain: If the cancer spreads to the bones.
Who can suffer from Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer primarily affects men. The risk increases with age, with most cases diagnosed in men over 50. Other factors that may increase the risk include:
- Family history: A family history of prostate cancer can increase the risk.
- Race: African American men have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer.
- Diet: A diet high in red meat and processed foods may increase the risk.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk.
What are the type of Prostate Cancer ?
Prostate cancer can be classified based on its aggressiveness and how it spreads:
- Adenocarcinoma: The most common type, accounting for almost all cases.
- Transitional cell carcinoma: Less common, usually occurring in men who have had radiation therapy for bladder cancer.
- Small cell carcinoma: Rare and aggressive, often spreading quickly.
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Rare, typically occurring in older men.
Which diagnostic are available for the Prostate Cancer?
· Digital rectal exam (DRE): A doctor inserts a finger into the rectum to feel the prostate gland for any abnormalities.
· Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: A blood test to measure the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland.
· Biopsy: A small sample of prostate tissue is removed for examination under a microscope.
· Imaging tests: CT scans, MRI scans, or bone scans may be used to assess the extent of the cancer.
What are the treatment of the Prostate Cancer ?
The treatment for prostate cancer depends on the stage of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and his preferences. Options include:
- Active surveillance: For low-grade cancers, monitoring the cancer without immediate treatment.
- Surgery: Removing the prostate gland (prostatectomy).
- Radiation therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy: Blocking the production of male hormones, which can slow the growth of prostate cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Using drugs that target specific molecules involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells.
Which diet should I take ,if any ?
While there is no specific diet proven to prevent or treat prostate cancer, a healthy diet can support overall health. Consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is recommended. Some studies suggest that a diet rich in lycopene (found in tomatoes and watermelon) may be beneficial.
Which speciality of the doctor will Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer is typically treated by a urologist, a doctor who specializes in diseases of the urinary tract and male reproductive system.
In Prostate Cancer completely curable ?
The curability of prostate cancer depends on the stage of the disease at diagnosis and the effectiveness of the treatment. In early stages, prostate cancer can often be cured with surgery or radiation therapy. However, advanced-stage prostate cancer may be more difficult to treat and may not be curable.