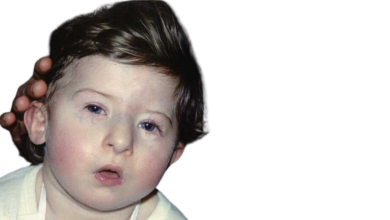
DiGeorge Syndrome: A genetic disorder affecting the heart, immune system, and facial features.

What is the DiGeorge Syndrome ?
DiGeorge syndrome, also known as velocardiofacial syndrome or 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, is a genetic condition caused by the deletion of a small piece of chromosome 22. This deletion affects the development of several organs and tissues in the body.
What are the symptom of DiGeorge Syndrome?
Symptoms of DiGeorge syndrome can vary widely, depending on the extent of the genetic deletion. Common symptoms include:
- Heart defects: These are the most common feature of DiGeorge syndrome and can range from mild to severe.
- Facial features: Characteristic facial features may include a small jaw, low-set ears, and a cleft palate.
- Thymic hypoplasia: A reduced or absent thymus gland, which is important for immune function.
- Hypoparathyroidism: A deficiency of parathyroid hormone, leading to low calcium levels in the blood.
- Learning disabilities and delays: These can affect cognitive development and behavior.
- Cleft palate or lip: A gap or opening in the roof or lip of the mouth.
- Hearing loss: This can be conductive or sensorineural.
- Kidney problems: These may include kidney stones or other abnormalities.
Who can suffer from DiGeorge Syndrome?
DiGeorge syndrome can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or race. It is not inherited from parents but rather occurs as a result of a new genetic mutation during the formation of the egg or sperm.
What are the type of DiGeorge Syndrome ?
There are several types of DiGeorge syndrome, based on the extent of the genetic deletion and the affected organs. These include:
- Full deletion: A complete deletion of the 22q11.2 region.
- Partial deletion: A smaller deletion that may affect fewer organs.
- Mosaic DiGeorge syndrome: Some cells have the deletion, while others do not.
Which diagnostic are available for the DiGeorge Syndrome ?
· Genetic testing: This is the definitive test for DiGeorge syndrome and involves examining a person’s chromosomes.
· Echocardiogram: This can be used to detect heart defects.
· Thyroid function tests: These can assess thyroid hormone levels.
· Calcium blood test: This can check for low calcium levels.
· Hearing test: This can assess hearing function.
· Kidney ultrasound: This can check for kidney abnormalities.
What are the treatment of the DiGeorge Syndrome ?
Treatment for DiGeorge syndrome depends on the specific symptoms and affected organs. It may include:
- Surgery: This may be necessary to correct heart defects or other abnormalities.
- Hormone therapy: This may be necessary to treat hypoparathyroidism or thyroid hormone deficiency.
- Immunotherapy: This may be necessary to boost the immune system.
- Physical therapy: This can help improve strength and coordination.
- Speech therapy: This can help with speech and language delays.
- Counseling: This can help individuals and families cope with the challenges of DiGeorge syndrome.
Which diet should I take ,if any ?
There is no specific diet recommended for people with DiGeorge syndrome. However, a healthy, balanced diet is important for overall health.
Which speciality of the doctor will DiGeorge Syndrome?
Individuals with DiGeorge syndrome may need to see a variety of specialists, including:
- Pediatrician: For general care and monitoring.
- Geneticist: To diagnose and manage the condition.
- Cardiologist: To address heart defects.
- Endocrinologist: To manage hormone levels.
- Immunologist: To address immune system problems.
- Physical therapist: To improve strength and coordination.
- Speech therapist: To address speech and language delays.
- Counselor: To provide emotional support.
In DiGeorge Syndrome completely curable ?
There is no cure for DiGeorge syndrome, but with appropriate medical care and support, individuals with the condition can lead fulfilling lives. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life.