What is the Hemophilia ?
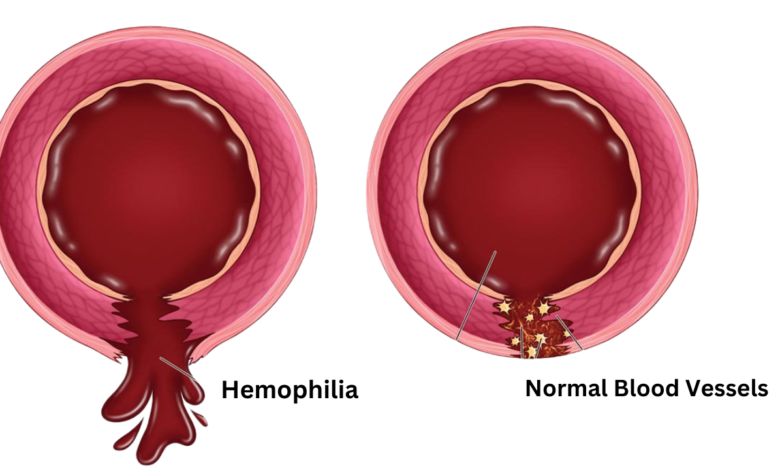
Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that affects the blood’s ability to clot. It is caused by a deficiency in clotting factors, proteins that help blood to clot.
What are the symptom of Hemophilia?
People with hemophilia may experience:
- Excessive bleeding after injuries or surgery
- Spontaneous bleeding into joints, muscles, or other tissues
- Nosebleeds
- Easy bruising
- Bleeding into the brain (hemorrhagic stroke)
Who can suffer from Hemophilia?
Hemophilia is primarily a genetic disorder that is inherited from parents. It is more common in males than females.
What are the type of Hemophilia?
There are two main types of hemophilia:
- Hemophilia A: This is the most common type, caused by a deficiency in clotting factor VIII.
- Hemophilia B: This is caused by a deficiency in clotting factor IX.
Which diagnostic are available for the Hemophilia ?
· Blood tests: These tests can measure the levels of clotting factors in the blood.
· Genetic testing: This can confirm the presence of the gene mutation that causes hemophilia.
What are the treatment of the Hemophilia ?
The treatment for hemophilia involves replacing the missing clotting factor. This can be done through:
- Infusion therapy: The clotting factor is infused into the bloodstream.
- Gene therapy: This is a newer treatment that involves replacing the defective gene that causes hemophilia.
Which diet should I take ,if any ?
There is no specific diet recommended for people with hemophilia. However, a healthy and balanced diet is important for overall health.
Which speciality of the doctor will Hemophilia?
A hematologist is a doctor who specializes in treating blood disorders, including hemophilia.
In Hemophilia completely curable ?
Currently, there is no cure for hemophilia. However, with proper treatment, people with hemophilia can live relatively normal lives. Gene therapy may offer hope for a cure in the future.